Two heterozygous red flowers white flowers are recessive are crossed – The cross between two heterozygous red flowers and recessive white flowers sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This exploration delves into the fascinating realm of genetic inheritance, unraveling the intricate interplay between genes, alleles, and their profound influence on the traits we observe in the world around us.
As we embark on this journey, we will witness the power of Punnett squares, which serve as invaluable tools for predicting the probability of offspring inheriting specific traits. We will delve into the genetic basis of flower color inheritance, uncovering the secrets behind why white flowers exhibit recessive characteristics.
Furthermore, we will unravel the intricate relationship between genotype and phenotype, shedding light on how genetic makeup manifests itself in observable traits.
Gene Inheritance and Expression
The inheritance of genetic traits is governed by the principles of Mendelian genetics. Heterozygosity refers to the presence of different alleles for a particular gene within an individual’s genotype. Dominant alleles are those that are expressed in the phenotype even when only one copy is present, while recessive alleles are only expressed when two copies are present.
For example, in the case of flower color, the allele for red flowers (R) is dominant over the allele for white flowers (r). If an individual has one copy of the R allele and one copy of the r allele (Rr), they will have a red flower phenotype, even though they carry the recessive allele for white flowers.
Punnett Square Analysis
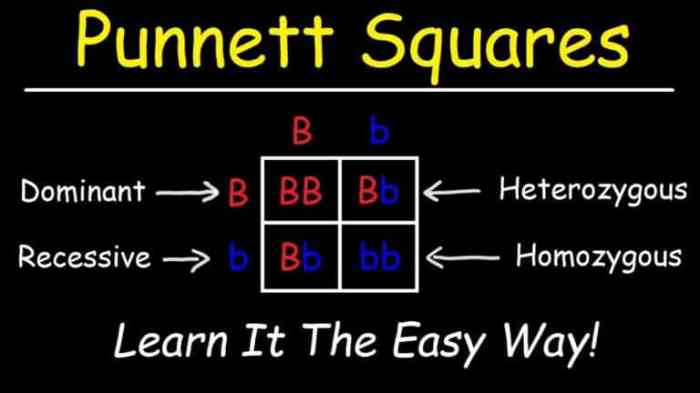
A Punnett square is a diagram that represents the possible offspring genotypes and phenotypes resulting from a cross between two parents. In the case of two heterozygous red flowers (Rr), the Punnett square would be as follows:
| R | r | |
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | Rr | rr |
The probability of obtaining offspring with different genotypes is as follows:
- RR: 25%
- Rr: 50%
- rr: 25%
The probability of obtaining offspring with different phenotypes is as follows:
- Red flowers: 75%
- White flowers: 25%
Flower Color Inheritance, Two heterozygous red flowers white flowers are recessive are crossed
The genetic basis of flower color inheritance is determined by the presence of pigments called anthocyanins. The R allele codes for the production of anthocyanins, while the r allele does not. Therefore, individuals with the RR or Rr genotype will have red flowers, while individuals with the rr genotype will have white flowers.
Genotype and Phenotype Relationships
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, while phenotype refers to the observable characteristics of an individual. In the case of flower color, the genotype determines the phenotype, with the R allele resulting in a red flower phenotype and the r allele resulting in a white flower phenotype.
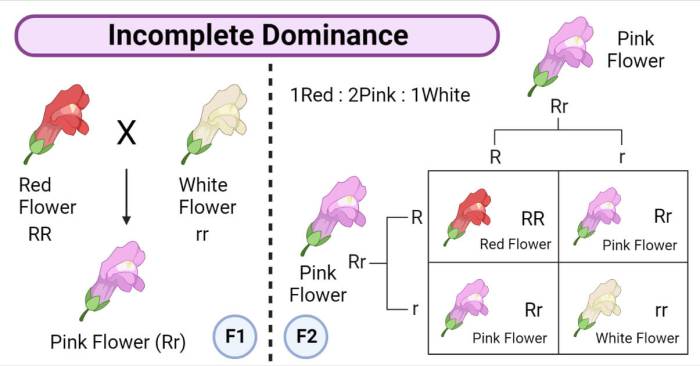
Incomplete dominance and codominance are two exceptions to the simple dominant-recessive relationship. In incomplete dominance, both alleles are expressed in the phenotype, resulting in an intermediate phenotype. In codominance, both alleles are expressed fully in the phenotype, resulting in a distinct phenotype that is different from either of the homozygous phenotypes.
Detailed FAQs: Two Heterozygous Red Flowers White Flowers Are Recessive Are Crossed
What is the probability of obtaining offspring with red flowers from the cross between two heterozygous red flowers?
The probability of obtaining offspring with red flowers is 75%.
Why are white flowers recessive in this scenario?
White flowers are recessive because they are only expressed when both alleles of the flower color gene carry the recessive allele. In contrast, red flowers are dominant and can be expressed even if only one allele of the flower color gene carries the dominant allele.
How does genotype influence phenotype in terms of flower color?
Genotype influences phenotype in terms of flower color by determining which alleles of the flower color gene are present in an individual. The genotype of an individual can be homozygous dominant (RR), homozygous recessive (rr), or heterozygous (Rr). Homozygous dominant individuals will have red flowers, homozygous recessive individuals will have white flowers, and heterozygous individuals will have red flowers due to the dominance of the red allele.