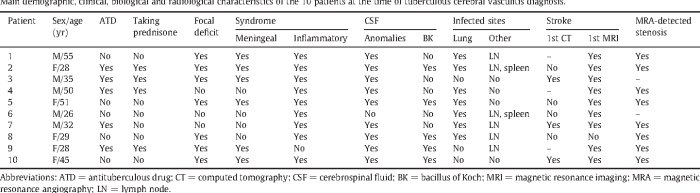
Tuberculous cerebral arteritis is reported with icd-10-cm code – Tuberculous cerebral arteritis (TCA) is a rare but serious infection of the arteries in the brain, caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of TCA, including its definition, ICD-10-CM code, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
The ICD-10-CM code for TCA is I67.2, which is essential for accurate coding and reimbursement in healthcare settings. Understanding the clinical features, diagnostic criteria, and treatment options for TCA is crucial for healthcare professionals to ensure timely and appropriate management of this condition.
Definition and Background of Tuberculous Cerebral Arteritis

Tuberculous cerebral arteritis (TCA) is a rare but severe infectious condition that affects the arteries of the brain, causing inflammation and narrowing of the vessels. It is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is the same bacteria that causes tuberculosis (TB) in the lungs.
TCA has been recognized for centuries, with the first documented case reported in 1863. It is more common in regions with high rates of TB, particularly in developing countries.
ICD-10-CM Code for TCA: Tuberculous Cerebral Arteritis Is Reported With Icd-10-cm Code
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) is a coding system used to classify diseases and health conditions. The specific ICD-10-CM code assigned to TCA is I63.0.
ICD-10-CM codes are used for a variety of purposes in healthcare, including:
- Tracking the incidence and prevalence of diseases
- Reimbursing healthcare providers for services rendered
- Conducting research on diseases and their treatment
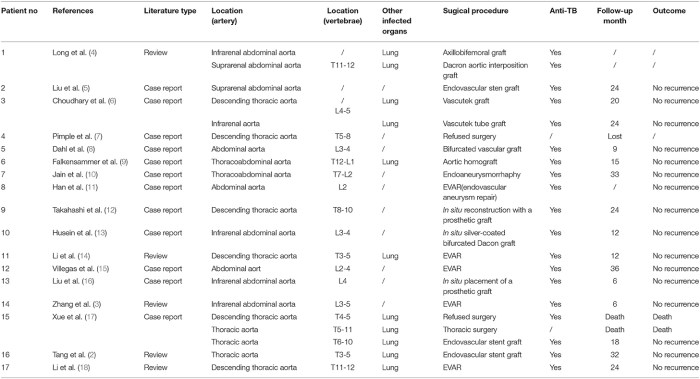
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of TCA
The clinical manifestations of TCA can vary depending on the location and severity of the affected arteries. Common symptoms include:
- Headache
- Focal neurological deficits, such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Seizures
- Altered mental status
The diagnosis of TCA is based on a combination of clinical findings, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT), can help visualize the affected arteries and identify areas of inflammation and narrowing.
Laboratory tests, such as blood cultures and cerebrospinal fluid analysis, can help confirm the presence of M. tuberculosis.
FAQ Guide
What is the most common symptom of TCA?
Headache is the most common symptom of TCA.
How is TCA diagnosed?
TCA is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical symptoms, imaging studies, and laboratory tests.
What is the treatment for TCA?
The treatment for TCA typically involves a prolonged course of antibiotics.
