Welcome to our comprehensive guide on periodic table trends worksheet answers. This guide will provide you with a thorough understanding of the periodic table, its trends, and how to answer worksheet questions related to them. Whether you’re a student looking to ace your next exam or a teacher seeking to enhance your lesson plans, this guide has everything you need.
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. Understanding the trends in the periodic table is crucial for predicting the behavior and properties of elements and their compounds.
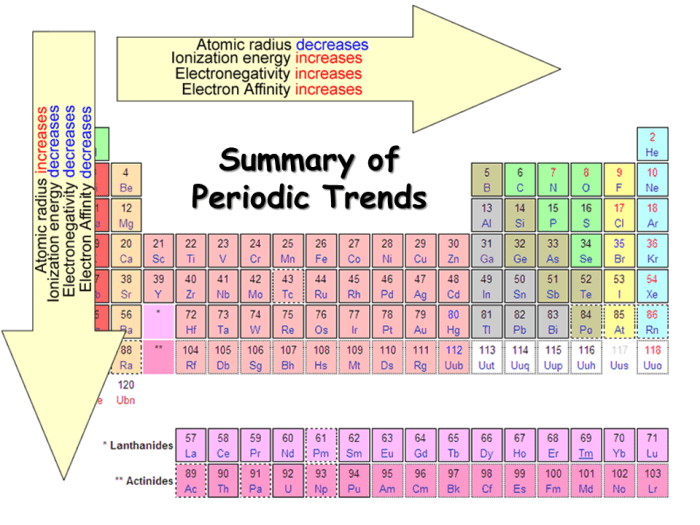
This guide will cover key periodic trends, including atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, electron affinity, and metallic character, providing you with a solid foundation in this essential area of chemistry.
Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Overview
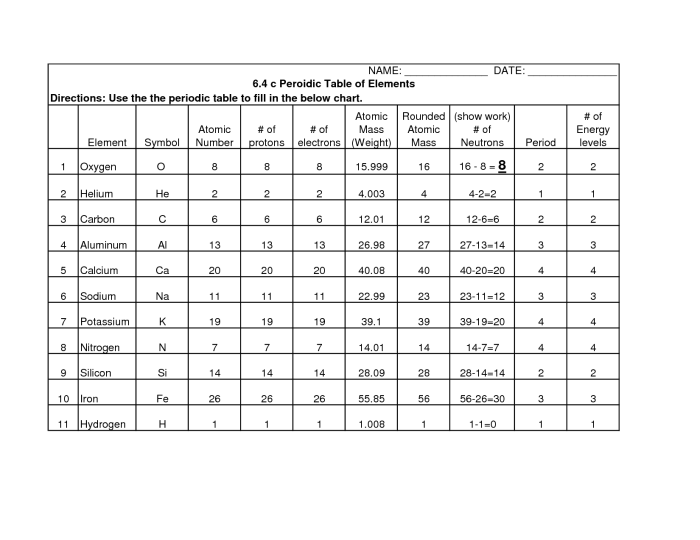
A periodic table trends worksheet is a tool designed to help students understand and analyze the patterns and trends exhibited by elements in the periodic table. It typically includes questions and exercises that guide students through the exploration of various periodic trends, such as atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, electron affinity, and metallic character.
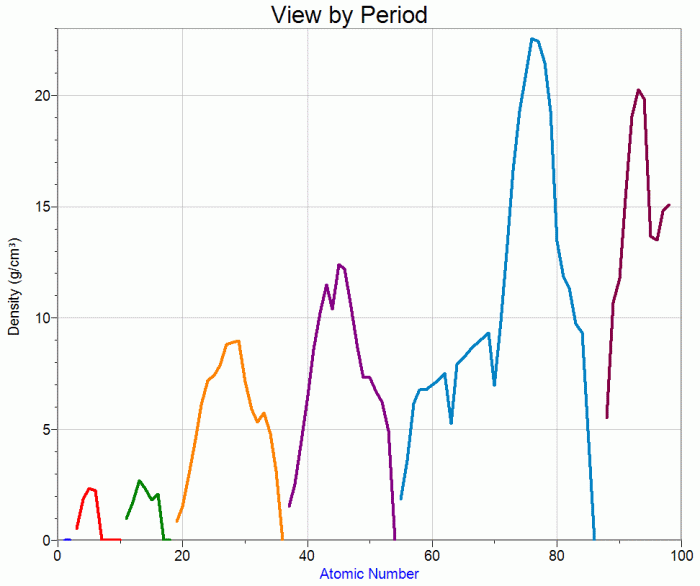
Atomic Radius
Atomic radius refers to the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell of an atom. It generally decreases across a period (row) from left to right and increases down a group (column) in the periodic table. This trend can be attributed to the increase in atomic number and effective nuclear charge across a period and the addition of new energy levels down a group.
Factors influencing atomic radius include:
- Atomic number: As the atomic number increases, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, leading to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons, resulting in a smaller atomic radius.
- Electron configuration: The presence of more electrons in the outermost energy level (valence electrons) can shield the inner electrons from the attraction of the nucleus, resulting in a larger atomic radius.
Ionization Energy
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state. It generally increases across a period from left to right and decreases down a group in the periodic table. This trend is primarily due to the increase in effective nuclear charge across a period and the addition of new energy levels down a group.
Factors influencing ionization energy include:
- Atomic number: As the atomic number increases, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, leading to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons, resulting in a higher ionization energy.
- Electron configuration: Electrons in higher energy levels are more loosely bound to the nucleus and thus require less energy to remove, resulting in a lower ionization energy.
Electronegativity, Periodic table trends worksheet answers
Electronegativity refers to the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. It generally increases across a period from left to right and decreases down a group in the periodic table. This trend can be attributed to the increase in effective nuclear charge across a period and the addition of new energy levels down a group.
Factors influencing electronegativity include:
- Atomic number: As the atomic number increases, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, leading to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons, resulting in a higher electronegativity.
- Electron configuration: Atoms with a higher number of valence electrons are less electronegative because they are more easily able to share or donate electrons.
Electron Affinity
Electron affinity is the energy change that occurs when an atom in its gaseous state gains an electron. It generally increases across a period from left to right and decreases down a group in the periodic table. This trend is primarily due to the increase in effective nuclear charge across a period and the addition of new energy levels down a group.
Factors influencing electron affinity include:
- Atomic number: As the atomic number increases, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, leading to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons, resulting in a higher electron affinity.
- Electron configuration: Atoms with a higher number of valence electrons have a lower electron affinity because they are less likely to accept an additional electron.
Metallic Character
Metallic character refers to the tendency of an element to exhibit metallic properties, such as luster, malleability, and ductility. It generally decreases across a period from left to right and increases down a group in the periodic table. This trend can be attributed to the increase in ionization energy across a period and the addition of new energy levels down a group.
Factors influencing metallic character include:
- Ionization energy: Elements with lower ionization energies are more likely to lose electrons and form positive ions, resulting in a higher metallic character.
- Atomic radius: Larger atoms have a lower ionization energy and thus a higher metallic character.
FAQ: Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Answers
What is the periodic table?
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties.
What are periodic trends?
Periodic trends are the patterns and regularities observed in the properties of elements as we move across the periodic table.
How can I use this guide to answer worksheet questions?
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of periodic table trends and how to answer worksheet questions related to them. By understanding these trends, you can use the information in this guide to help you answer specific worksheet questions.